Table of Contents
- Developer Guide
- Terminology
- Architecture
- Workflow
-
How To…
- Work with JSON Endpoints
- Create a Search Object with the API
- Create a Search Object with the "q=" URL Parameter
- Specify SearchProviders with the "providers=" URL Parameter
- Get synchronous results with the "qs=" URL Parameter
- Request date-sorted results from one or more SearchProviders
- Handle NOTted queries
- Subscribe to a Search
- Subscribe to a Search with M365 Sources
- Detect and Remove Duplicate Results
- Manage Search Objects
- Re-Run a Search
- Update a Search
- Add Spelling Correction
- Adjust Relevancy for a Single SearchProvider
- Expire Search Objects
- Manage Results
- Get Unified Results
- Page Through Results
- Get Search Times
- Configure Pipelines
- Configure Relevancy Field Weights
- Configure Stopwords Language
- Understand the Explain Structure
- Develop New Connectors
- Develop New Processors
- Develop New Mixers
- Retrieval Augmented Generation Web Socket API
- Using Query Transformations
- Example Search Objects
Developer Guide
Intended Audience
This guide is intended to provide developers with an overview of SWIRL and how to accomplish specific tasks with it. Please refer to the Developer Reference for lists of system states, system objects and properties, etc.
Terminology
| Word | Explanation |
|---|---|
| SearchProvider | An object defining some searchable source. It includes metadata identifying the type of connector used to search the source and more. |
| Search | An object defining a query that some user or system desires to have run. It includes the query_string with the actual text, and metadata. Most of the metadata is optional. |
| Query | Search engines make a distinction between the act of searching and what goes into a search. The user's keywords or other search terms are usually referred to as a query. SWIRL follows this convention whenever possible, but, at times, may refer to a search as a query. Sorry about that. |
| Subscribe | An important property of Search objects. When set to true, SWIRL will periodically re-run the search, specifying a date sort to get newer data, and removing duplicates from results. |
| Connector | A SWIRL module that can connect to, and query, a particular type of data source. Connectors are a wrapper around some existing Python package such as request.get or elasticsearch. |
| Processors | A SWIRL module that can process search (query) or result content in a source-specific or generic format. They transform whatever they accept in various ways - for example removing control characters from a search, or spell checking it, re-mapping source provider result formats to SWIRL's own - and more. |
| Pipelines | A process that executes pre-defined sequences of Processors. Each processor transforms whatever content it is asked to operate on. |
| Result | An object defining results from one SearchProvider during the federated search process in response to the creation of a Search object. It includes metadata about the SearchProvider. Much of the metadata is optional. |
| Mixer | A SWIRL module that organizes results from multiple SearchProviders into a unified result set. It includes metadata from all SearchProviders as well as the Search itself. |
| Relevancy Ranking | An estimation of the relative value of a given search engine result to the user's query, as compared to all others - to put it simply. For more information: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Relevance_(information_retrieval) |
Architecture
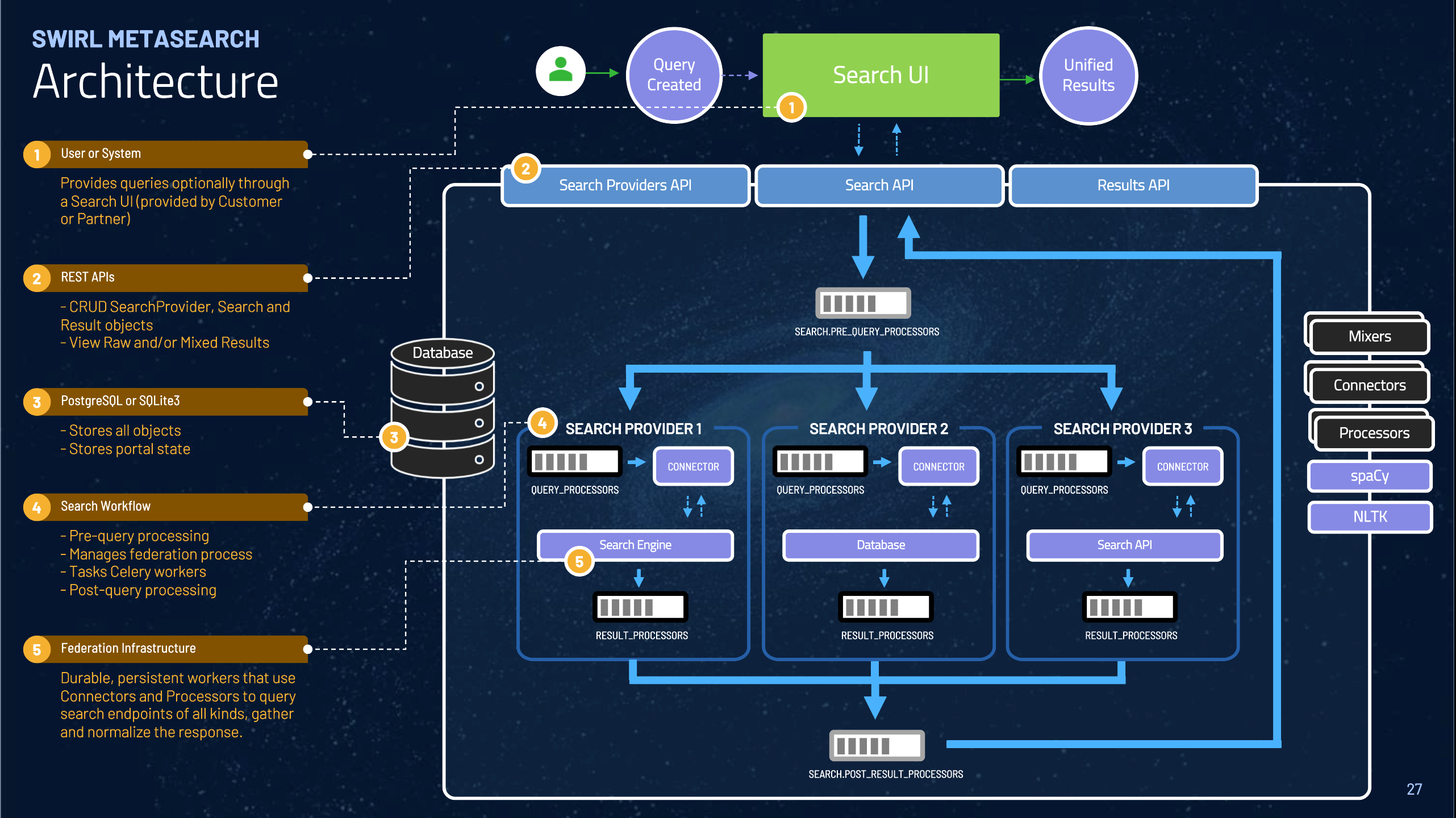
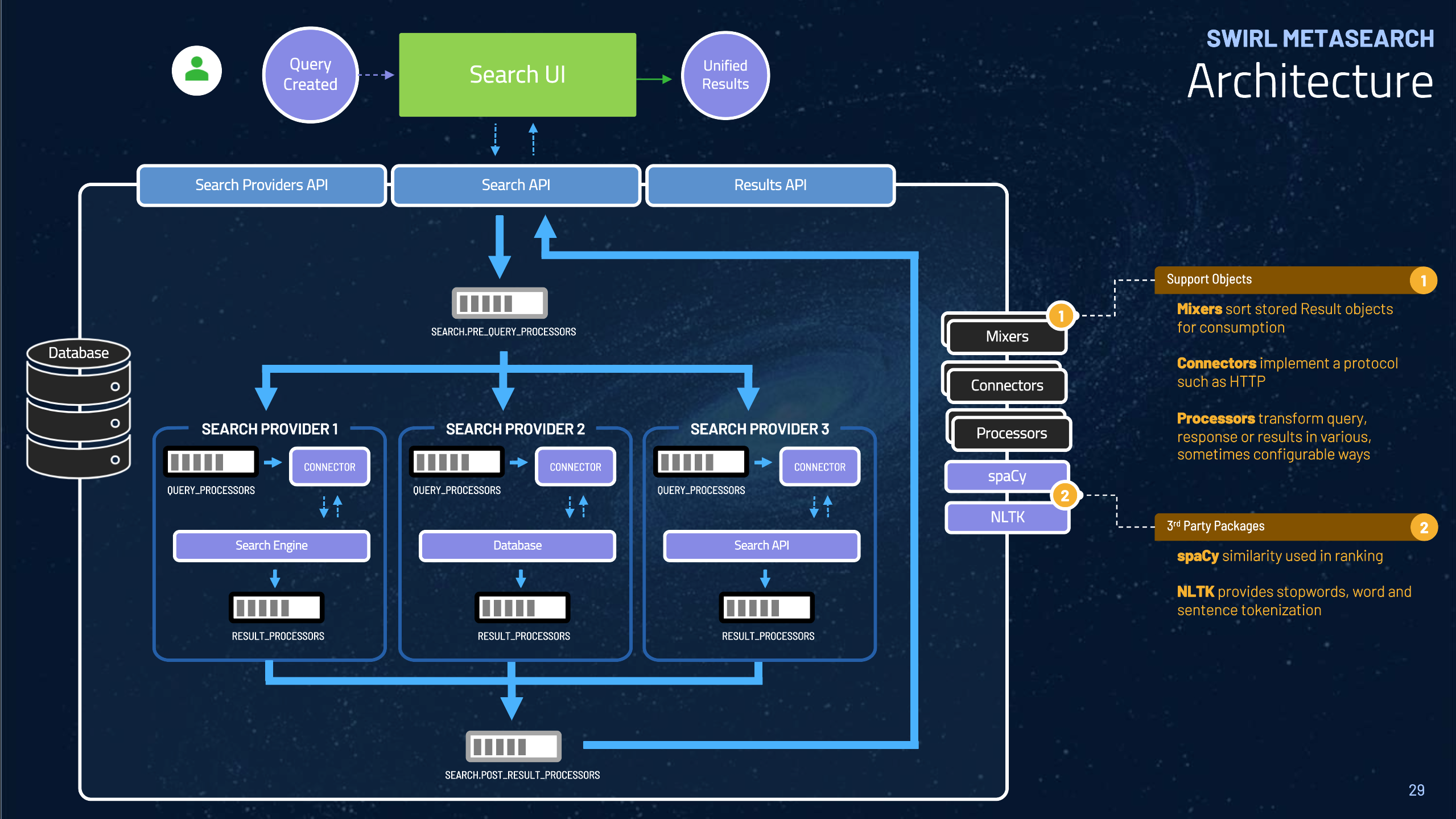
Workflow
-
Create a new
Searchobject at the endpoint/swirl/search/-
This invokes the create method in swirl/views.py.
-
SWIRL responds with the
idof the newly created Search object. Theview.pymodule creates the object, then invokes swirl/search.py which manages the federation process from there.
-
-
The search module swirl/search.py:
-
Executes pre-query processing, using the specified
Search.pre_query_processors. -
Executes the federation process by creating one federate_task for each SearchProvider specified.
-
-
Waits for all tasks to report success by polling the Search and Result objects in the database, or the configured
settings.SWIRL_TIMEOUTis reached.
 While the search module waits…
While the search module waits… -
Each
federate_taskcreates aConnectorobject. -
Each
Connectorobject executes the federation workflow for the specified SearchProvider, as follows:-
Executes query processing as specified in
Search.query_processors -
Constructs and validates the query for the SearchProvider using the
url,query_templateorquery_template_json, andquery_mappings -
Connects to the SearchProvider, sends the query, and gathers the response
-
Normalizes the response into result format - a list of dicts
-
Executes result processing as specified in
Search.result_processors -
Saves the results in the database
 When all the Connectors have written results, or
When all the Connectors have written results, or settings.SWIRL_TIMEOUTis reached:
-
-
search.pyinvokes the specifiedSearch.post_result_processors, and they finalize the results, including relevancy ranking and optionally duplicate detection. -
search.pysets theSearch.statustoFULL_RESULTS_READYorPARTIAL_RESULTS_READY
 Anytime after this…
Anytime after this… -
To retrieve results go to the
Resultsendpoint/swirl/results-
All the
Resultobjects will appear. Individual ones can be retrieved by adding theidto the Result URL. -
Adding
search_idto the Result URL invokes theSearch.result_mixer. Mixers read theResultobjects from a single Search, (which are linked bysearch_id), and organize them as appropriate.
-
-
To continuously update results, set the
Search.subscribeproperty totrue.-
SWIRL will periodically run each
SearchwithSearch.subscribe, settingSearch.sorttodate, merging and de-duplicating new results. -
New result items can be retrieved by using the
Search.new_results_urlor selecting aNewItemmixer.
-
How To…
Work with JSON Endpoints
If using a browser with SWIRL API endpoints, including the URLs in this guide, we recommend turning off any browser prefetch, to avoid creating multiple objects using SWIRL's ?q= and ?qs= parameters.
Create a Search Object with the API
-
Go to http://localhost:8000/swirl/search/
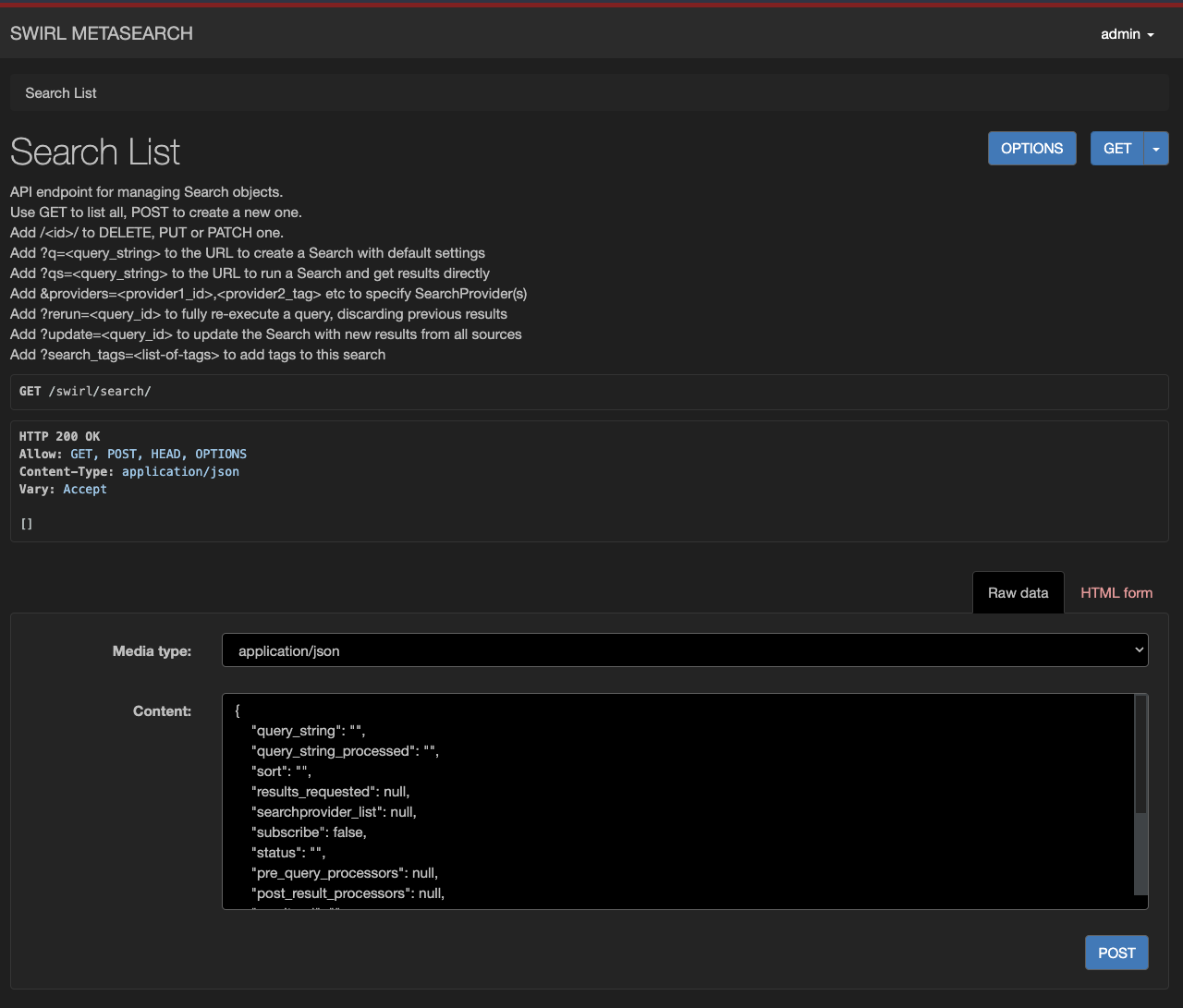
- Go to the form at the bottom of the page
- Change the form to
Raw datamode and clear any pre-built input - Copy/paste an example from above
- Press the POST button
SWIRL will respond with the newly created Search Object, including the id for it:
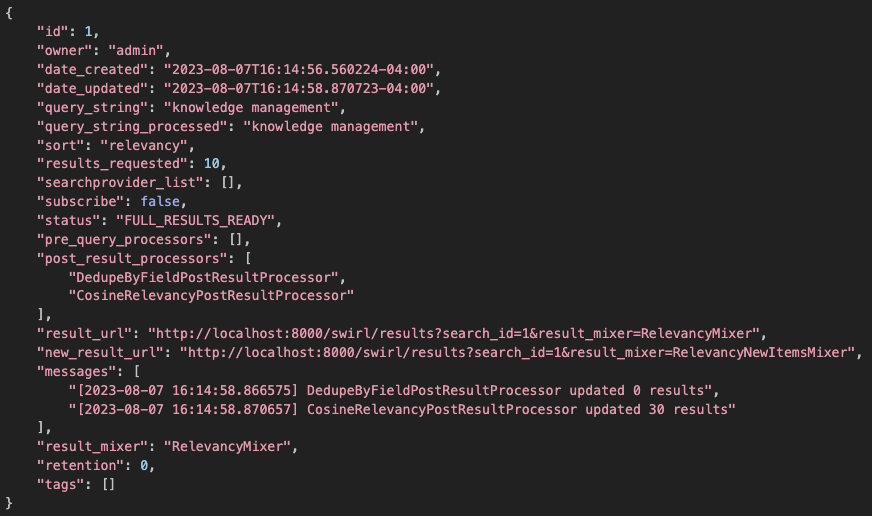
Note the id value down. It's required in the next step to get unified, relevancy ranked results.
Create a Search Object with the "q=" URL Parameter
To create a Search object and specify only a query_string and otherwise accepting the defaults, add ?q=your-query-string to the API URL.
For example: http://localhost:8000/swirl/search?q=knowledge+management
After a few seconds, SWIRL will redirect you to the fully mixed results page:
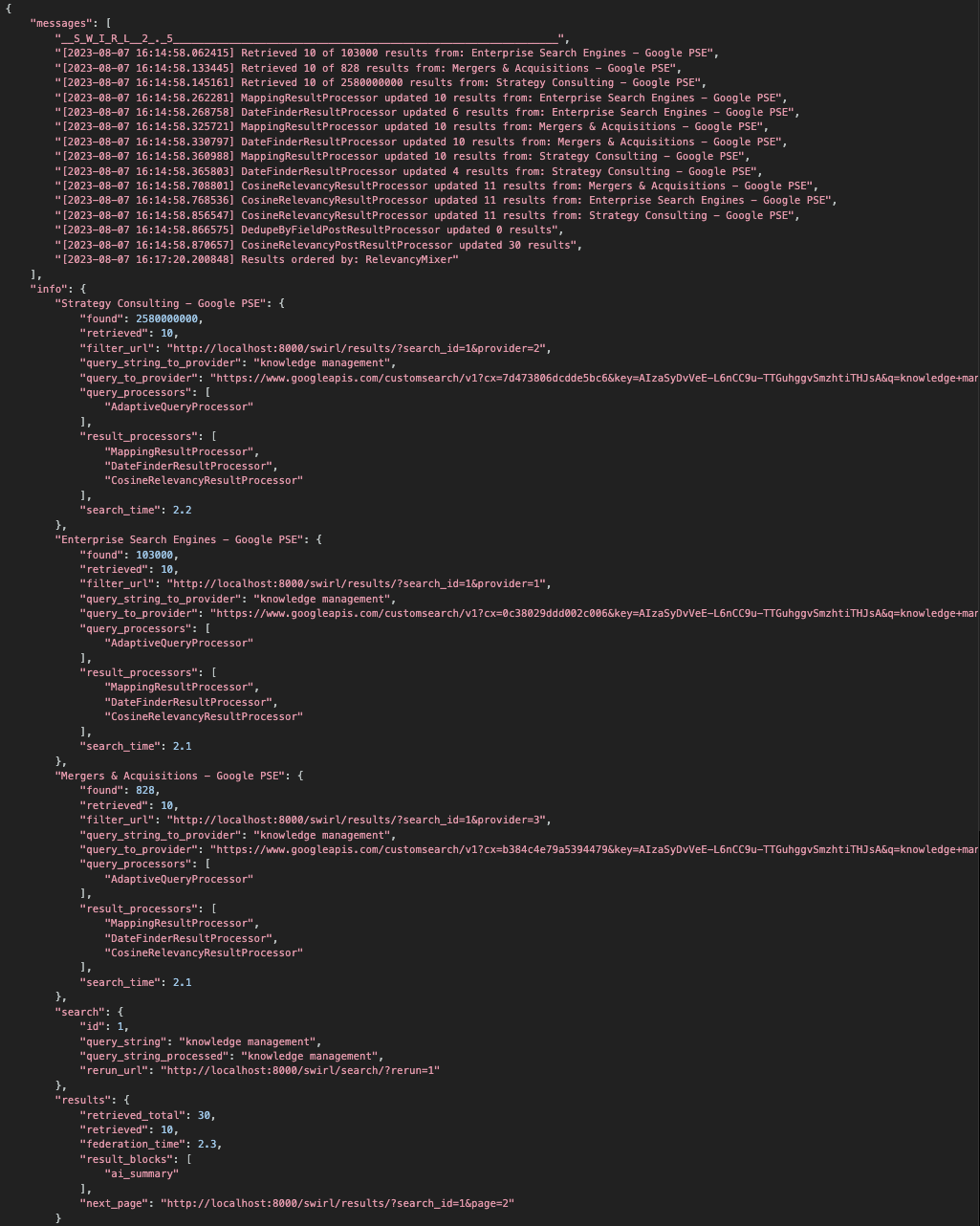
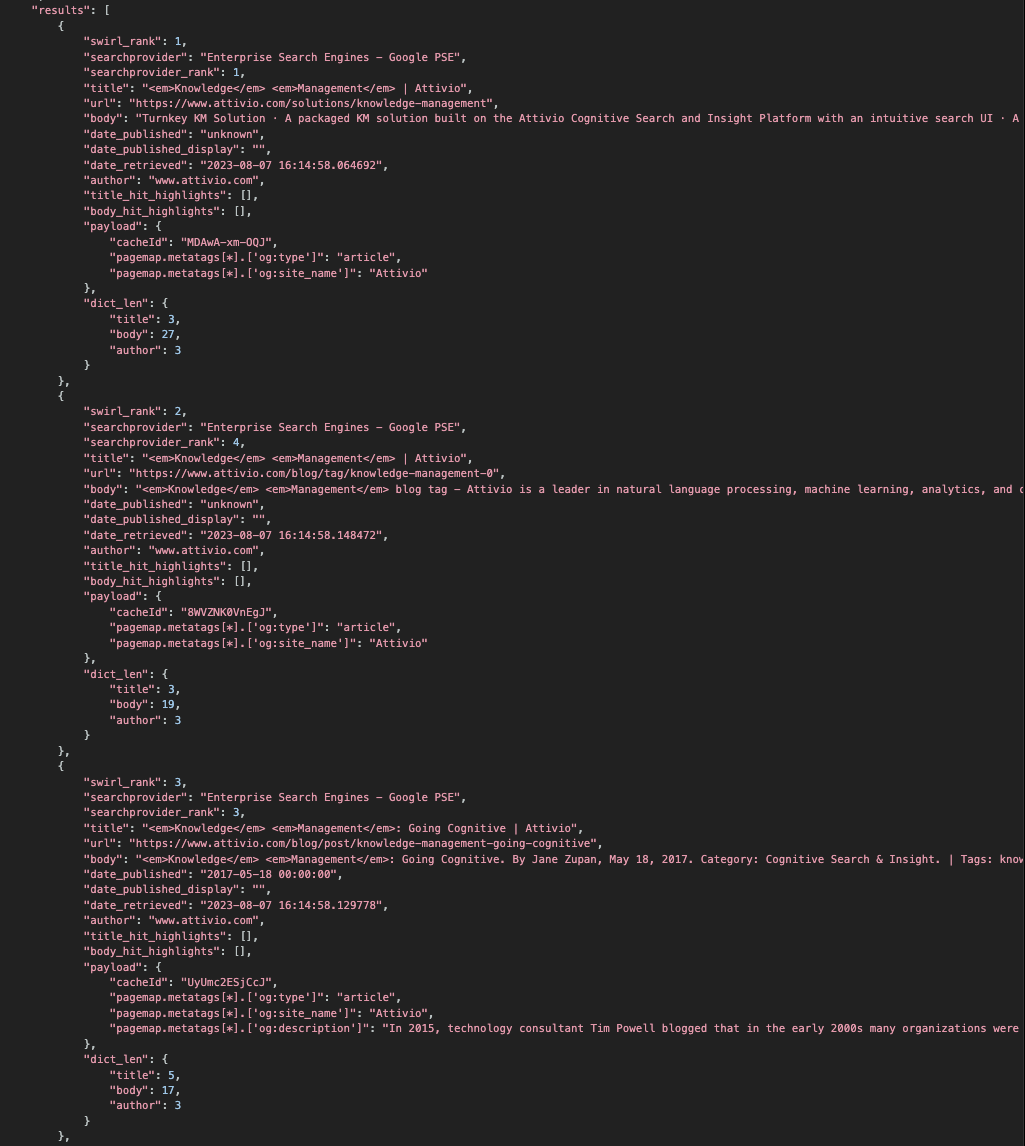
There are some limitations to the q= interface:
- You must URL encode your query; for text queries, this mostly means turning spaces into plus-signs. Use a free URL encoder for help with this: https://www.freeformatter.com/url-encoder.html
- All active and default SearchProviders are queried
- Error handling is limited; if no results appear check the Search object by opening:
http://localhost:8000/swirl/search/<your-search-id>
Specify SearchProviders with the "providers=" URL Parameter
As of version 1.6, the providers= URL parameter is now supported. It accepts a list of SearchProvider Tags, or just a single one. For example:
http://localhost:8000/swirl/search/?q=knowledge+management&providers=maritime
To specify a list of Tags:
http://localhost:8000/swirl/search/?q=knowledge+management&providers=maritime,news
Get synchronous results with the "qs=" URL Parameter
The qs= parameter works like the q= parameter does (see above), except that it returns the first page of results (only) to the caller directly, with no polling of the Search object or handling of a redirect required.
For example: http://localhost:8000/swirl/search?qs=knowledge+management
The qs= parameter can also be used with the providers and result_mixer parameters.
As of SWIRL 3.1.0, RAG processing is now available through a single API call using qs=, e.g. ?qs=metasearch&rag=true.
As of SWIRL 3.2.0, the default AI Summary timeout value can also be overridden with a URL parameter in the Galaxy UI. For example: http://localhost:8000/galaxy/?q=gig%20economics&rag=true&rag_timeout=90000
Note that &page= is NOT supported with qs=; to access the second page of results use the next_page property from the info.results structure.
"results": {
"retrieved_total": 30,
"retrieved": 10,
"federation_time": 2.2,
"result_blocks": [
"ai_summary"
],
"next_page": "http://localhost:8000/swirl/results/?search_id=2&page=2"
}
Request date-sorted results from one or more SearchProviders
If "sort": "date" is specified in the Search object, SWIRL connectors that support date sorting will request results in that order. By default SWIRL will still relevancy rank these results, presenting a cross section of the freshest results from all providers.
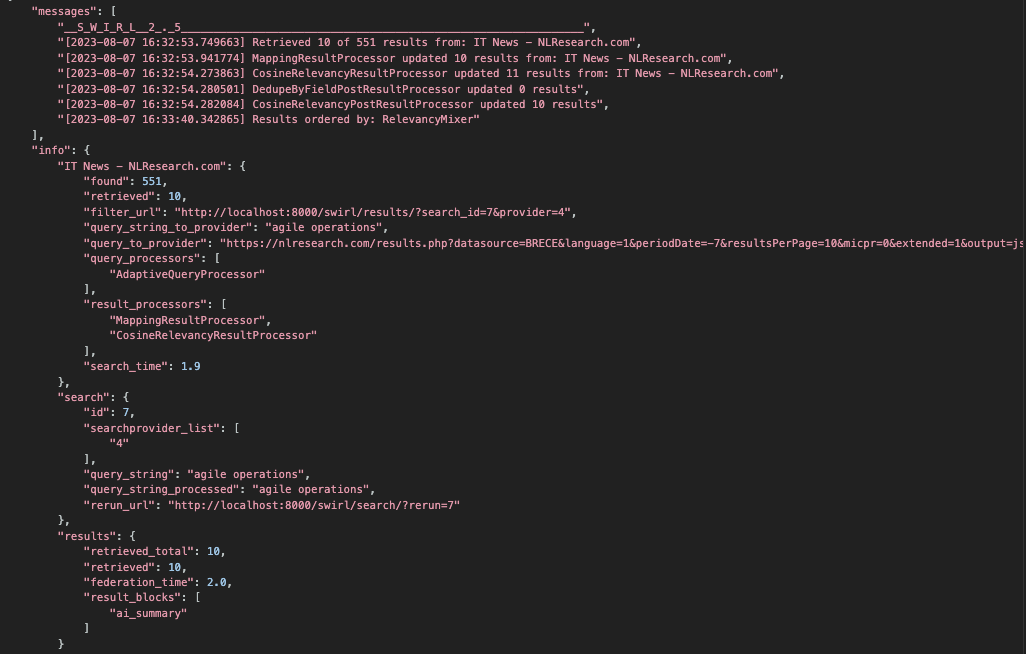
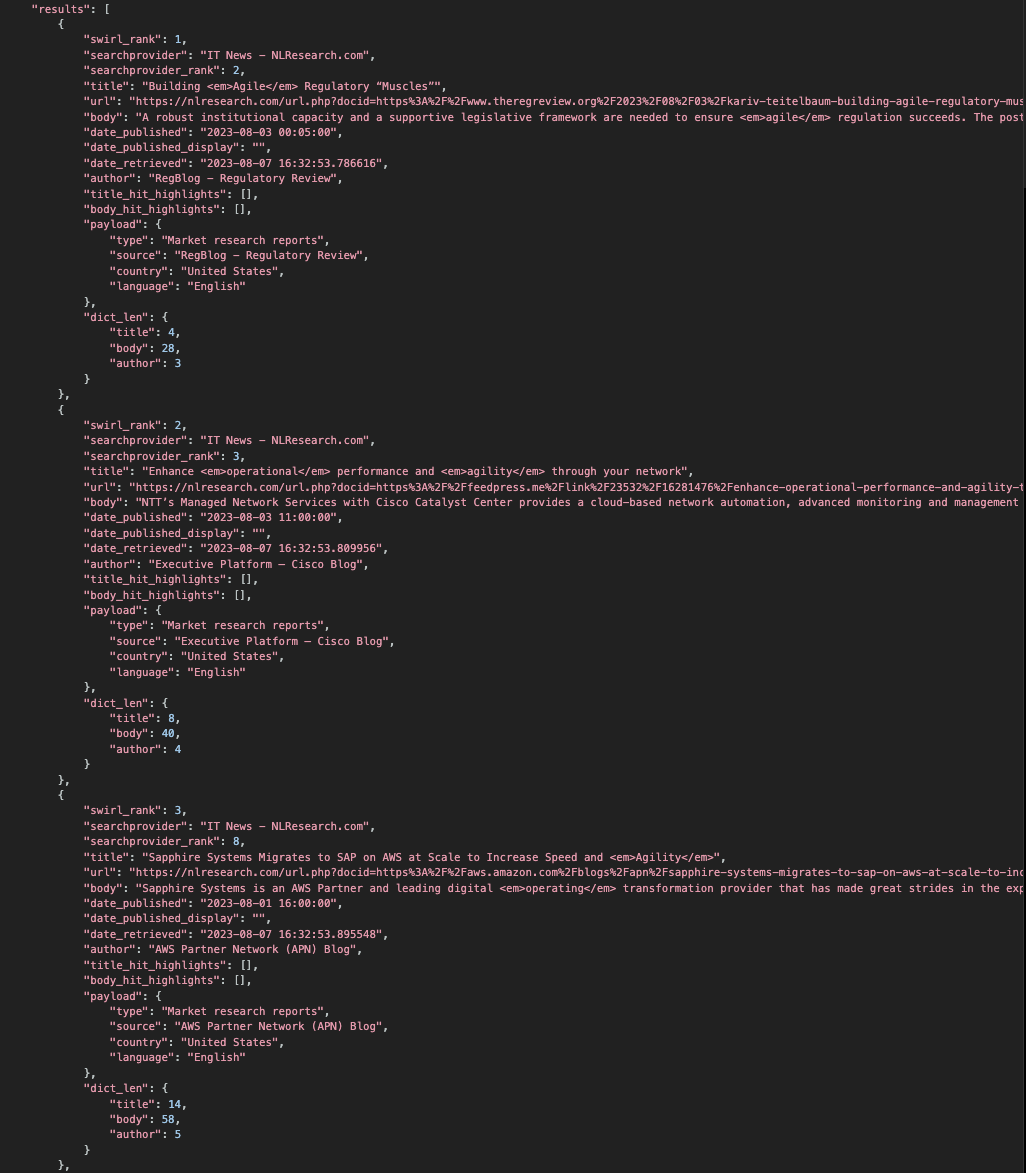
NOTES:
- In Release 2.5, the
DateFindingResultProcessorwas added to the Google PSE SearchProvider JSON. It finds a date in a large percentage of results that otherwise wouldn't have one, and copies the date to thedate_publishedfield. - Some sources simply won't report a date published, but still send a different response.
Handle NOTted queries
Should a SearchProvider include a NOT'ted term in a result, a message is placed in the Relevancy Explain. For example, here is an example result for the query generative ai NOT chatgpt which returned the term chatgpt anyway, failing to honor the NOT:
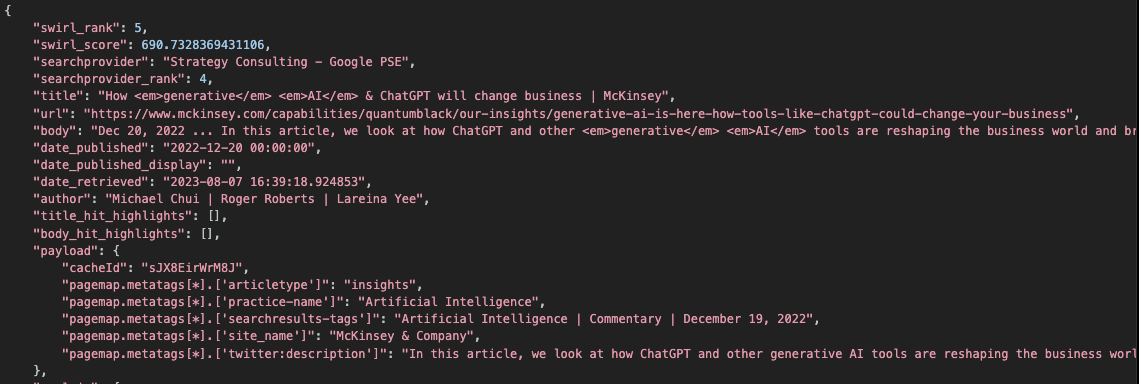
One way to address this is to make sure the NOT query-mapping is set correctly for that provider.
Subscribe to a Search
Search objects have a subscribe property. If set to true, SWIRL will update the Search every four hours, setting the sort property to date in order to favor new results.
For example:
{
"id": 10,
"owner": "admin",
"date_created": "2023-08-07T16:51:41.391574-04:00",
"date_updated": "2023-08-07T16:52:49.395218-04:00",
"query_string": "electric vehicles NOT tesla",
"query_string_processed": "electric vehicles NOT tesla",
"sort": "relevancy",
"results_requested": 10,
"searchprovider_list": [],
"subscribe": true,
"status": "FULL_RESULTS_READY",
"pre_query_processors": [],
"post_result_processors": [
"DedupeByFieldPostResultProcessor",
"CosineRelevancyPostResultProcessor"
],
"result_url": "http://localhost:8000/swirl/results?search_id=10&result_mixer=RelevancyMixer",
"new_result_url": "http://localhost:8000/swirl/results?search_id=10&result_mixer=RelevancyNewItemsMixer",
"messages": [
"[2023-08-07 16:51:43.648034] DedupeByFieldPostResultProcessor updated 0 results",
"[2023-08-07 16:51:43.651454] CosineRelevancyPostResultProcessor updated 30 results"
],
"result_mixer": "RelevancyMixer",
"retention": 0,
"tags": []
}
The post_result_processors specification above includes detecting and removing duplicates by exact match on a specified field.
SWIRL will set the status to "FULL_UPDATE_READY" when finished updating. New results will have a field new which will be set to 1. Use the new_result_url to retrieve only the new results via the ResultNewItemsMixer or DateNewItemsMixer, depending on the sort specified.
{
"id": 10,
"owner": "admin",
"date_created": "2023-08-07T16:51:41.391574-04:00",
"date_updated": "2023-08-07T17:00:02.011144-04:00",
"query_string": "electric vehicles NOT tesla",
"query_string_processed": "electric vehicles NOT tesla",
"sort": "date",
"results_requested": 10,
"searchprovider_list": [],
"subscribe": true,
"status": "FULL_UPDATE_READY",
"pre_query_processors": [],
"post_result_processors": [
"DedupeByFieldPostResultProcessor",
"CosineRelevancyPostResultProcessor"
],
"result_url": "http://localhost:8000/swirl/results?search_id=10&result_mixer=RelevancyMixer",
"new_result_url": "http://localhost:8000/swirl/results?search_id=10&result_mixer=RelevancyNewItemsMixer",
"messages": [
"[2023-08-07 16:51:43.648034] DedupeByFieldPostResultProcessor updated 0 results",
"[2023-08-07 16:51:43.651454] CosineRelevancyPostResultProcessor updated 30 results",
"[2023-08-07 16:55:02.161868] DedupeByFieldPostResultProcessor deleted 2 results",
"[2023-08-07 16:55:02.166261] CosineRelevancyPostResultProcessor updated 58 results",
"[2023-08-07 17:00:02.006126] DedupeByFieldPostResultProcessor deleted 30 results",
"[2023-08-07 17:00:02.010975] CosineRelevancyPostResultProcessor updated 58 results"
],
"result_mixer": "RelevancyMixer",
"retention": 0,
"tags": []
}
The messages part of the Search object will contain messages from the federation process. The Result objects from each SearchProvider contain messages from that source.
Use the NewItems Mixers to view only new results for a Search.
Subscribe to a Search with M365 Sources
To subscribe to a Search that contains any Microsoft SearchProviders, follow these steps BEFORE setting the subscribe field to true on the Search object.
- Enter this URL into a browser to open the SWIRL homepage: http://localhost:8000/swirl/

-
Click on
Admin -
Log in as the user who owns the Search object you want to subscribe
-
Return to the SWIRL homepage, and then click
Authenticators
If you don't see the Microsoft option on this page, make sure that at least one M365 SearchProvider enabled ("active": true) before proceeding to the next step.
-
Click the
Refresh Tokenbutton

-
Log in to your Microsoft account, if prompted to do so
-
Return to the SWIRL Search object and set
"subscribe": trueon that Search
Detect and Remove Duplicate Results
SWIRL includes two PostResultProcessors that can detect and remove duplicates.
| Processor | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| DedupeByFieldResultProcessor | Detects duplicates by identical match on a single field, and deletes them | The field is specified in swirl_server/settings.py and the default field is url
|
| DedupeBySimilarityResultProcessor | Detects duplicates by similarity threshold, and deletes them | The similarity considers the title and body fields, and the threshold is set in swirl_server/settings.py
|
The DedupeByFieldResultProcessor in included in the default Search.post_result_processors pipeline. To change this modify the getSearchPostResultProcessorsDefault method in swirl/models.py.
Manage Search Objects
You can edit any Search by adding the id to the end of the /swirl/search URL. For example: http://localhost:8000/swirl/search/1/
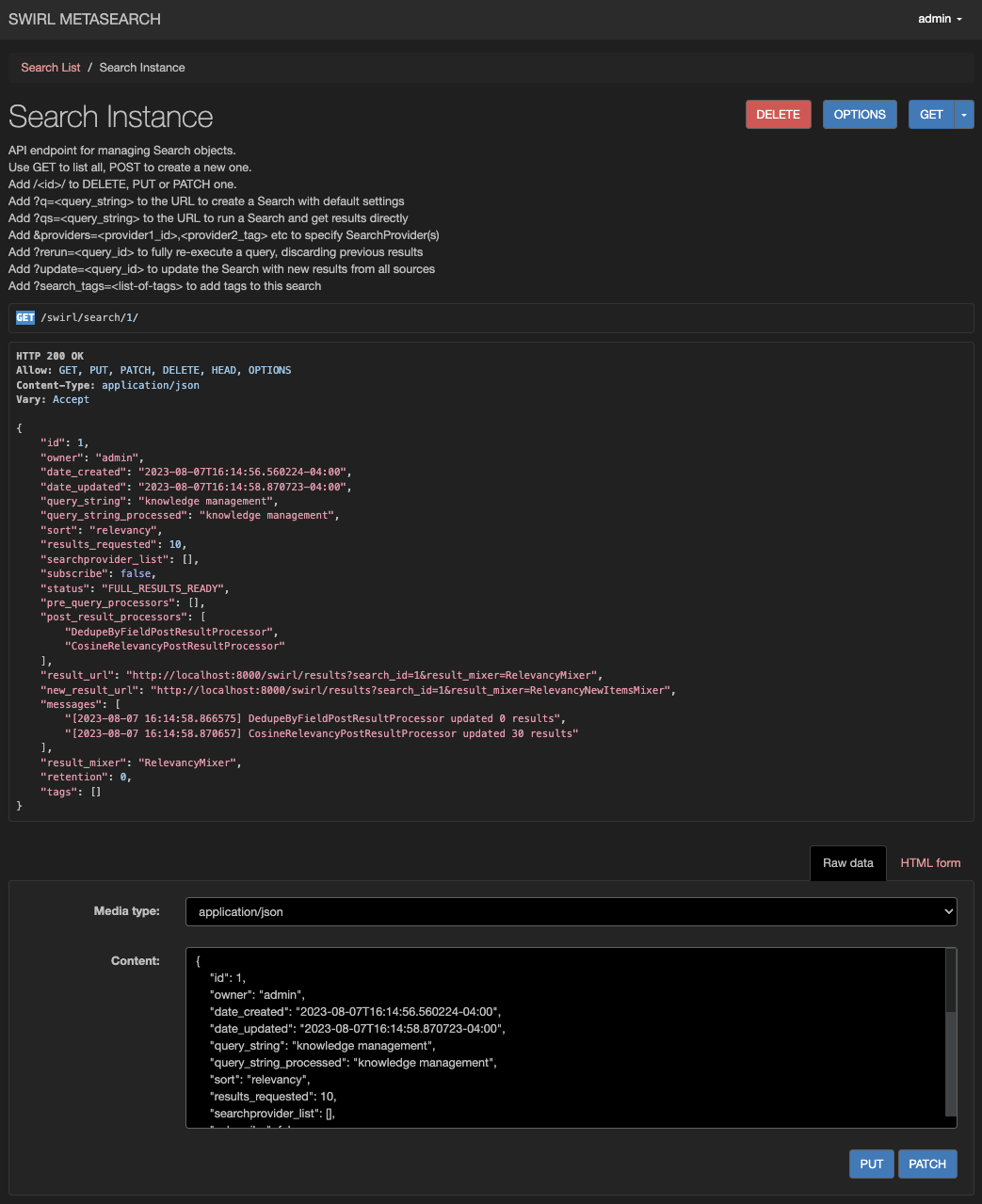
From here, you can use the form to:
- DELETE it, forever
- Edit the body of the request and PUT it back
If you delete a Search, the associated Result objects are immediately deleted as well. This may be changed in a future release.
Re-Run a Search
The re-run option is available to handle failed searches, partial results, changes to relevancy, or SearchProvider configuration changes.
| Method | Description | Example URL |
|---|---|---|
| Re-run | Discards any previous results and re-runs the Search | http://localhost:8000/swirl/search?rerun=1 |
This URL is provided by SWIRL in every mixed result set, in the info.search block of the response.
Update a Search
To re-run a Search, but add new results to the previous ones, run an update:
http://localhost:8000/swirl/search/?update=<search-id>
The update will change the Search.sort to "date" prior to running, to favor new results. SWIRL will also de-duplicate results using the url field, by default. As the update proceeds, SWIRL will update the Search and Result message fields as appropriate, along with the result counts.
Use the RelevancyNewItemsMixer and DateNewItemsMixer to retrieve new, updated results.
Add Spelling Correction
To specify spelling correction for the Search.query_string, add this option to the Search object:
"pre_query_processors": ["SpellcheckQueryProcessor"],
Corrections are provided by TextBlob which is claimed to be at most ~70% accurate.
If you want to apply spellcheck to a single SearchProvider, put it in that SearchProvider's query_processors property instead.
Use Spellcheck cautiously as it tends to cause a lack of results from sources that have sparse indexes and limited or no fuzzy search.
Adjust Relevancy for a Single SearchProvider
SWIRL 3.2.0 includes a new RequireQueryStringInTitleResultProcessor. If installed after the MappingResultProcessor it will drop results that don't include the user's query in the title.
This processor is intended for use with sources like LinkedIn that frequently return related profiles that mention a person, but aren't about them. (SWIRL will normally rank these results poorly, but this will eliminate them entirely.)
Expire Search Objects
If your SWIRL installation is using the Search Expiration Service, users can specify the retention setting for each Search.
The following table describes the Search.retention field:
| Retention Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 0 | Retain indefinitely, do not expire |
| 1 | Retain for 1 hour |
| 2 | Retain for 1 day |
| 3 | Retain for 1 month |
The exact time of expiration is determined by the Celery Beat Configuration and the Search Expiration Service configuration.
Manage Results
To delete a result Object - for example if you re-run a Search - add the id of the Result to the Result URL. For example: http://localhost:8000/swirl/results/1/
From here, you can use the form to:
- DELETE it, forever
- Edit the body of the request and PUT it back
If you delete a Result set, it will not delete the associated Search.
Get Unified Results
Result Mixers organize Result objects from multiple SearchProviders into unified result sets.
Mixers operate only on saved Results - not live/raw federated data - and can be safely run again and again. The mixed output will immediately reflect any changes in Result data - for example if re-running a search.
To retrieve the unified results for a Search, add ?search_id= and the id of the Search to the Result API endpoint. For example: http://localhost:8000/swirl/results?search_id=1
SWIRL will respond with results organized by the result_mixer specified in the Search object.


Specify a different Mixer on-the-fly by adding the URL parameter result_mixer. For example: http://localhost:8000/swirl/results?search_id=1&result_mixer=Stack1Mixer
Page Through Results
SWIRL by default requests at least 10 results per SearchProvider, and stores them in its local SQLite3 database. To page through results, add a page parameter to the Results URL. For example:
For example: http://localhost:8000/swirl/results?search_id=1&page=2
If you need more mixed results, increase the results_per_query value in the SearchProvider configuration. A setting of 20 or 50 or 100 will ensure that you have lots of results to page through with the mixer. Since SWIRL will only page through saved Results, re-run the query with a higher results_per_query value in each SearchProvider to get more results.
Get Search Times
SWIRL reports each source's search time in the relevant info block of the response:
"info": "Enterprise Search (web/Google PSE)": {
"found": 8640,
"retrieved": 10,
...
"search_time": 2.1
},
The overall search time is reported in the info.results block:
"results": {
"retrieved_total": 50,
"retrieved": 10,
"federation_time": 3.2,
"next_page": "http://localhost:8000/swirl/results/?search_id=507&page=2"
}
The timings are in seconds, and rounded to the nearest 0.1.
The federation time includes query, response, connection, querying, response, result and post-result processing time. Mixer time is not included in federation time.
Configure Pipelines
In SWIRL 2.5, result processing was separated into two passes. The SearchProvider.result_processors runs first, followed by the Search.post_result_processors which adjusts length and finalizes. Example result_processors configuration from a Google PSE SearchProvider:
"result_processors": [
"MappingResultProcessor",
"DateFinderResultProcessor",
"CosineRelevancyResultProcessor"
],
The default Search.result_mixer is the RelevancyMixer.
To change these, modify swirl/models.py and change the Search.getSearchPostResultProcessorsDefault().
To change the default mixer, change the default in the Search.result_mixer:
result_mixer = models.CharField(max_length=200, default='RelevancyMixer', choices=MIXER_CHOICES)
Configure Relevancy Field Weights
To configure the weights for individual SWIRL fields, modify the RELEVANCY_CONFIG dictionary in the swirl_server/settings.py file.
The defaults are:
| Field | Weight | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| title | 1.5 | |
| body | 1.0 | Base relevancy score |
| author | 1.0 |
Configure Stopwords Language
As of version 1.6, SWIRL is configured to load English stopwords only. To change this, modify SWIRL_DEFAULT_QUERY_LANGUAGE in swirl_settings/settings.py and change it to another NLTK stopword language.
Understand the Explain Structure
The CosineRelevancyProcessor outputs a JSON structure that explains the swirl_score for each result. It is displayed by default; to hide it add &explain=False to any mixer URL.
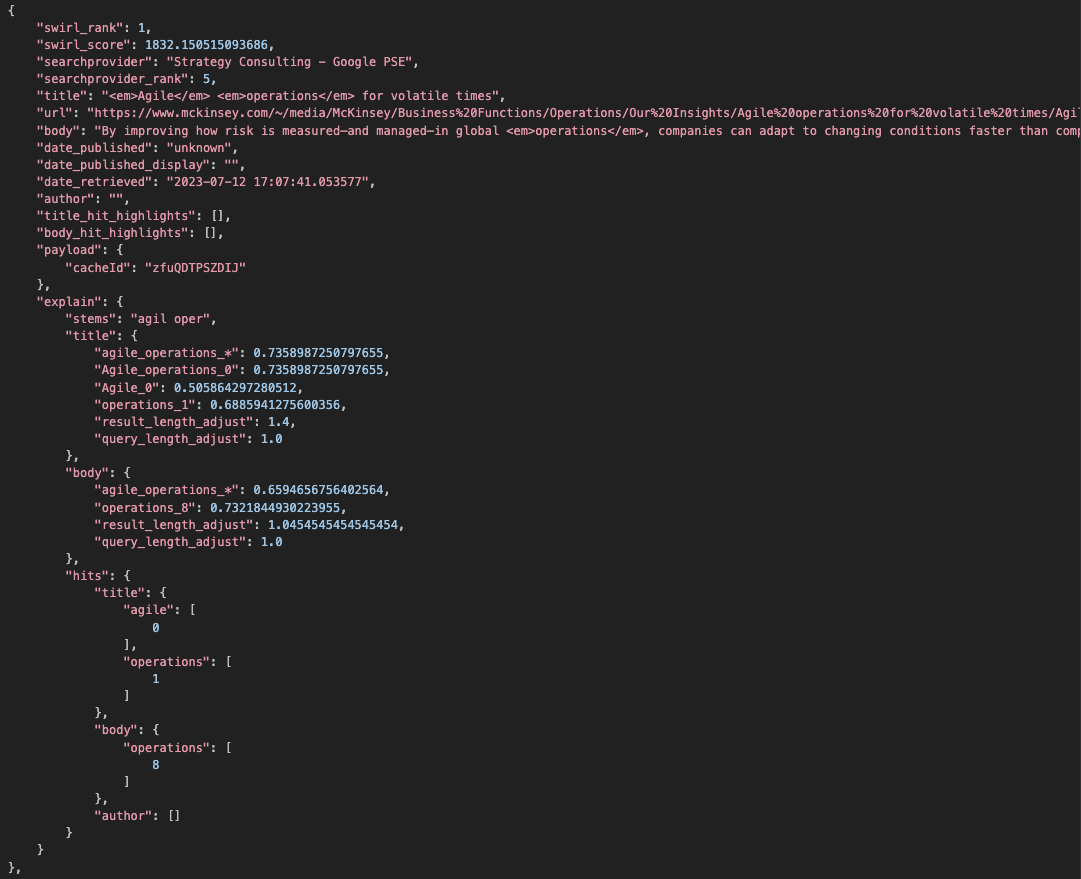
The following table explains the meaning of each match:
| Postfix | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
_* | Entire query matched, at least partially, against the entire result field | "knowledge_management_*", .73323667.. |
_s* | Entire query matched, at least partially, one or more sentences, and this is the maximum similarity | "knowledge_management_s*", .73323667.. |
_n | A part of the query matched at word position 'n' in the field | "Knowledge_Management_0", .73323667.. |
For queries that include a match position, the actual match terms are extracted and highlighted.
The structure also includes matching stems ("stems"), result and query length adjustments as noted above, and a structure called "hits" that identifies the zero-offset token count for each match.
Develop New Connectors
To connect to a new endpoint for an existing Connector - like RequestsGet - create a new SearchProvider instead. The Google PSE SearchProvider example JSON shows how to use one connector to make hundreds of SearchProviders!
To search against a new API where there is a high quality Python package and/or a unique data transport not already supported - then write a new Connector.
The base classes are here: swirl/connectors.
Each Connector is responsible for a workflow defined in the base class federate() method:
def federate(self):
'''
Executes the workflow for a given search and provider
'''
self.start_time = time.time()
if self.status == 'READY':
self.status = 'FEDERATING'
try:
self.process_query()
self.construct_query()
v = self.validate_query()
if v:
self.execute_search()
if self.status not in ['FEDERATING', 'READY']:
self.error(f"execute_search() failed, status {self.status}")
if self.status == 'FEDERATING':
self.normalize_response()
if self.status not in ['FEDERATING', 'READY']:
self.error(f"normalize_response() failed, status {self.status}")
else:
self.process_results()
if self.status == 'READY':
res = self.save_results()
if res:
return True
else:
return False
else:
self.error(f"process_results() failed, status {self.status}")
return False
else:
self.error(f'validate_query() failed: {v}')
return False
# end if
except Exception as err:
self.error(f'{err}')
return False
# end try
else:
self.error(f'unexpected status: {self.status}')
return False
# end if
The following table explains each stage executed by each Connector:
| Stage | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| process_query | Calls the specified processor to adapt/transform the query for this SearchProvider | |
| construct_query | Assembles the final form query for the source | |
| validate_query | Attempts to verify that the query should produce results, if there are any, and is free of syntax errors | Returns False if the query_to_provider` is not valid |
| execute_search | Connects to the defined SearchProvider, issues the query, and stores the response | |
| normalize_response | Transforms the SearchProvider response into a JSON result set that SWIRL can use | |
| process_results | Calls the specified processor to transform the JSON results into the SWIRL result format | |
| save_results | Stores the normalized results in the Django database |
A connector is expected to override execute_search and normalize_response, at minimum. For more information, review the Connector base class.
The "eval_credentials": "", option can be used to set a credential variable in the session and then utilize it in the SearchProvider configuration. For example, if you set session['my-connector-token'], SWIRL will take that variable and replace it with the {credentials} string in the SearchProvider.
{
...
eval_credentials: 'session["my-connector-token"]',
credentials: 'myusername:{credentials}'
}
NOTES:
- Import new connectors in
swirl/connectors/__init__.py - Add new processors to the appropriate CHOICES section of swirl/models.py - note this will require database migration
- Connectors should only import the objects required for a single connection - for example requests, Elastic or SQLite3
- To implement a variation on an existing transport, derive a class from it, then override just the
normalize_responsemethod. - Make sure the new
execute_querymethod:- Supports
results_per_query> 10, including automatic paging if needed - Supports date sorting, if the source repository does
- Supports
- Develop
query_mappingsincluding especiallyDATE_SORT,PAGE,NOT_CHARandNOT - Results from each source should be processed with a result processor, ideally the MappingResultProcessor.
Develop New Processors
Processors objects are defined in swirl/processors. They are designed to be executed in sequence. Each should perform one set of transformations and no more.
To create a new processor, derive it from Query, Result or PostResultProcessor. Override the process() method for simple changes, or derive new ones by adding variables to __init__. Be sure to validate() them. Processors MUST return either the processed data or, for PostResultProcessors, an integer indicating how many results were updated.
The following table describes the classes available:
| Processor | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| AdaptiveQueryProcessor | Handles query adaptation using query_mappings
| Default |
| MappingResultProcessor | Prepares results using result_mappings
| Default |
| CosineRelevancyPostResultProcessor | Performs relevancy ranking of Results | |
| DedupeByFieldPostResultProcessor | Detects and removes duplicates from Results by exact match on a specified field | |
| DedupeBySimilarityPostResultProcessor | Detects and removes duplicates from Results by Cosine Similarity | |
| GenericQueryProcessor | Removes special characters | |
| GenericResultProcessor | Copies response to result by exact field name match (e.g. title) | |
| DateFinderResultProcessor | Looks for a date in the body field of each result item. Should it find one, and the date_published for that item is 'unknown', it replaces date_published with the date extracted from the body, and notes this in the result.messages. |
NOTES:
- Import new processors in
swirl/processors/__init__.py - Add new processors to the appropriate
CHOICESpart of swirl/models.py - note this will require database migration - Only
PostResultProcessorsshould access model data - Make sure the
process()method returns data or a count of the number of results updated - Helper functions to create Result dictionaries and highlight text are located in swirl/processors/utils.py
Develop New Mixers
Mixers are located in swirl/mixers. They implement the following workflow:
def mix(self):
'''
Executes the workflow for a given mixer
'''
self.order()
self.finalize()
return self.mix_wrapper
Most variations on Mixers override the order() method. All order() has to do is save self.all_results in some new order, as self.mixed_results. For example:
def order(self):
'''
Orders all_results into mixed_results
Base class, intended to be overridden!
'''
self.mixed_results = self.all_results[(self.page-1)*self.results_requested:(self.page)*self.results_requested]
Here's the RelevancyMixer:
class RelevancyMixer(Mixer):
type = 'RelevancyMixer'
def order(self):
# sort by score
self.mixed_results = sorted(sorted(self.all_results, key=itemgetter('searchprovider_rank')), key=itemgetter('swirl_score'), reverse=True)
The finalize() method trims the self.mixed_results to the appropriate page, adds metadata, and returns the mix_wrapper structure. So long as there are enough results, the Mixer will page through them.
Notes:
- Import new mixers in
swirl/mixers/__init__.py - Add new mixers to the appropriate
CHOICESsection ofswirl/models.py- note this will require database migration
Retrieval Augmented Generation Web Socket API
WebSocket Interaction Protocol for UI Developers
Available as of SWIRL 3.0: This section outlines the protocol for WebSocket interactions with the SWIRL server.
- Initialize the WebSocket
- Action: Create a WebSocket connection.
-
Parameters:
-
searchId: SWIRL unique identifier of a search -
ragItems: Optional array of integer that identify an individual search result in the search result of the search.
-
-
Behavior: Initializes a new WebSocket connection. Send the initial information (like
searchIdandragItems) to the server. This setup is required before any data exchange can happen. NOTE: Necessary authentication should be handled before attempting to establish a WebSocket connection. This might involve sending a token or other credentials.
- Sending Data
- Action: Send a RAG message over the WebSocket connection.
-
Parameters:
-
data: Can be either an empty message, which initiates the RAG processing or astopcommand. Stop will cleanly shutdown the currently running RAG for the search ID used in establishing the connection.
-
- Receiving Data
- Action: Receive rag result data from the WebSocket connection.
-
Return Value: A JSON RAG result with the following structure, or simple
No dataif no response was available due to error:{ 'message': { 'date_published':<timestamp-response-creation> 'title':<query-string>, 'body':<ai_response>, 'author':'ChatGPT' 'searchprovider':'ChatGPT' 'searchprovider_rank':1 'result_block':'ai_summary' 'rag_query_items':[<list-of-rag-items-passed-in>] } }
- Connection Teardown
- Action: Properly close the WebSocket connection.
- Behavior: Closes the WebSocket connection gracefully.
Using Query Transformations
Query Transformation Rules
As of SWIRL 2.0, developers can apply a set of transformation rules to a query using the new Query Transformation feature.
The rules can be applied for all sources (pre-query) or to individual sources (query). There are three transformation types:
- Replace - Replace one string in the query w/ another or with nothing, essentially remove the term.
- Synonym - Replace a term with an OR of the original term and the synonyms
- Synonym Bag - Replace a term with an OR of all synonyms
Rules for the three types of supported transformations are expressed in terms of CSVs that are uploaded to SWIRL.
Replace/Rewrite
- Column 1 - A semi-colon separated list of patterns to replace. Limited use of wild cards is supported: non-leading star character.
- Column 2 - String to replace the patterns with.
Note: For the use case of removing a term DO NOT add a comma after the first column, and there can be only 1 term for this usage.
Example configuration:
# column1, column2
mobiles; ombile; mo bile, mobile
computers, computer
cheap* smartphones, cheap smartphone
on
Example results:
| query | transformation |
|---|---|
| mobiles | mobile |
| ombile | mobile |
| mo bile | mobile |
| on computing | computing |
| cheaper smartphones | cheap smartphone |
| computers go figure | computer go figure |
Synonym
- Column 1 - Term
- Column 2 - Synonym
Example configuration:
# column1, column2
notebook, laptop
laptop, personal computer
pc, personal computer
personal computer, pc
car, ride
Example results:
| query | transformation |
|---|---|
| notebook | (notebook OR laptop) |
| pc | (pc OR personal computer) |
| personal computer | (personal computer OR pc) |
| I love my notebook | I love my (notebook OR laptop) |
| This pc, it is better than a notebook | This (pc OR personal computer) , it is better than a (notebook OR laptop) |
| My favorite song is "You got a fast car" | My favorite song is " You got a fast (car OR ride) " |
Synonym Bag
- Column 1 - Term
- Column 2..N - List of Synonyms
Example configuration:
# column1..columnN
notebook, personal computer, laptop, pc
car,automobile, ride
Example results:
| query | transformation |
|---|---|
| car | (car OR automobile OR ride) |
| automobile | (automobile OR car OR ride) |
| ride | (ride OR car OR automobile) |
| pimp my ride | pimp my (ride OR car OR automobile) |
| automobile, yours is fast | (automobile OR car OR ride) , yours is fast |
| I love the movie The Notebook | I love the movie The Notebook |
| My new notebook is slow | My new (notebook OR personal computer OR laptop OR pc) is slow |
Uploading a Query Transformation CSV
Go to the SWIRL homepage and make sure you're logged in as an admin user.
Select the Upload Query Transform CSV option:

Enter a Name for the CSV and select a Type value:

Choose the CSV file to upload:

Select the Upload button:

After this, you can now use the uploaded CSV in pre-query or query processing by referencing it as: <name>.<type>
So, for the CSV uploaded above, the reference would be: TestQueryTransform.synonym
Pre-Query Processing
Adding a pre-query processor can be done in one of two ways:
- The
pre_query_processorparameter can be used when running the search through the REST API. For example:
/api/swirl/search/search?q=notebook&pre_query_processor=TestQueryTransform.synonym
- The SWIRL Search Object's
pre_query_processorsfield can be updated to include the reference to the query transform. See the User Guide for details on creating a search object with the API.
Query Processing
Update the Search Provider's query_processors field to include the reference. For example:
{
"name": "TEST Enterprise Search (web/Google PSE) with qxr query_processor",
"active": "true",
"default": "true",
"connector": "RequestsGet",
"url": "https://www.googleapis.com/customsearch/v1",
"query_template": "{url}",
"query_processors": [
"AdaptiveQueryProcessor",
"TestQueryTransform.synonym"
],
"query_mappings": "cx=0c38029ddd002c006,DATE_SORT=sort=date,PAGE=start=RESULT_INDEX,NOT_CHAR=-",
"response_mappings": "FOUND=searchInformation.totalResults,RETRIEVED=queries.request[0].count,RESULTS=items",
"result_processors": [
"MappingResultProcessor",
"CosineRelevancyResultProcessor"
],
"result_mappings": "url=link,body=htmlSnippet,cacheId,NO_PAYLOAD",
"results_per_query": 10,
"credentials": "key=",
"tags": [
"News",
"EnterpriseSearch"
]
}
Integrate Source Synonyms Into SWIRL Relevancy
As of SWIRL 1.10, you can use hit highlight extraction to integrate a SearchProvider's synonym hits into SWIRL's relevancy processing.
Data source synonym configuration can compromise the accuracy of SWIRL's relevancy scoring because the relevancy PostResultProcessor isn't aware of terms used to retrieve documents that were not part of the original query. As of Release 1.10, SWIRL can surface any terms used by the SearchProvider to match documents in the results returned by that source.
The following SearchProviders may be configured with synonym support at the source and require this additional configuration in SWIRL:
- OpenSearch
- Elastic
- Solr
Configuration
- Update the default SearchProvider configuration to add hit highlighting to the source fields that are mapped to SWIRL's
titleandbodyfields.
Exactly how to do this will vary based on the original search engine and the use case, but to enable highlighting on every field, add the following to the query_template field of the SearchProvider:
'highlight': { 'fields': { '*': {} } },
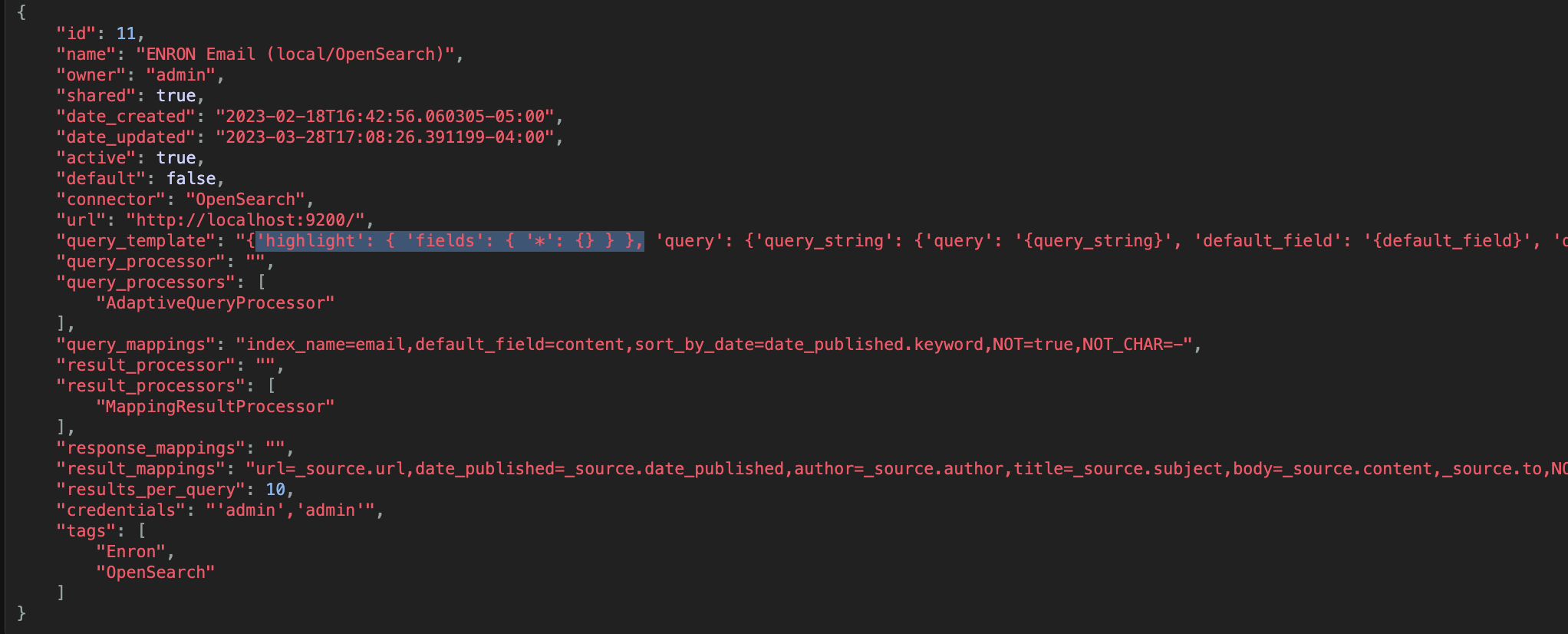
Consult the documentation for the original search engine for other way this could be accomplished.
- In the
results_mappingfield of the SearchProvider, assign the SWIRL fieldsbody_hit_highlightsandtitle_hit_highlightsto the JSON reference in which the source's hit highlighting resides.
For example, for the following result:
{
"_source" : {
"url" : "blair-l/sent_items/605.",
"date_published" : "2001-08-02 16:08:06.000000",
"author" : "Blair, Lynn </O=ENRON/OU=NA/CN=RECIPIENTS/CN=LBLAIR>",
"to" : "Scott, Donna </O=ENRON/OU=NA/CN=RECIPIENTS/CN=Dscott1>",
"subject" : "Laptop computer",
"content" : "\t\tDonna, I need one laptop computer for Terry or John to use when they\tare out of town. Please put them on the list. Thanks. Lynn"
},
"highlight" : {
"subject" : [
"<em>Laptop</em> computer"
],
"content" : [
"Donna, I need one <em>laptop</em> computer for Terry or John to use when they\tare out of town."
]
}
}
…assign body_hit_highlights and title_hit_highlights as follows in the results_mapping field:
title_hit_highlights=highlight.subject, body_hit_highlights=highlight.content

Results
The above configuration would be reflected in the info section of the Results for this SearchProvider:
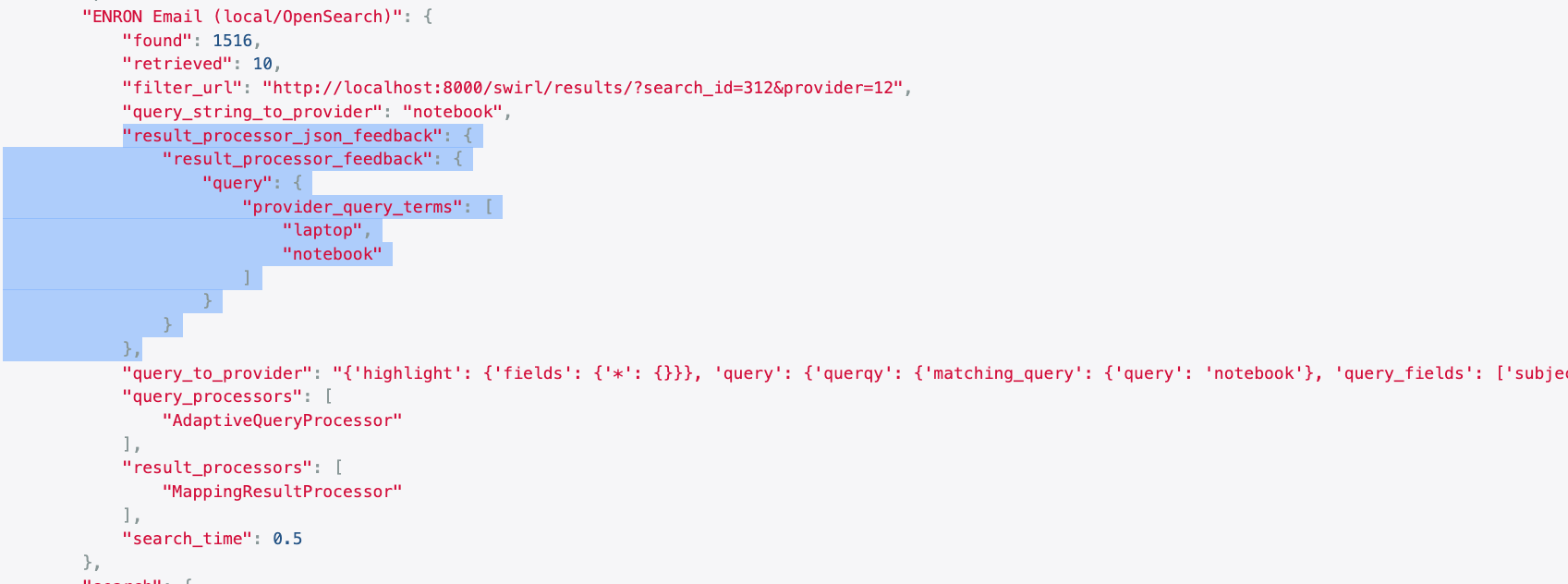
In this example, the query term was "notebook". Within the results_processor_json_feedback field of the info block, there is a JSON structure called results_processor_feedback.query.provider_query_terms that contains a list of query terms. One of these terms is "notebook" while the other is "laptop". This is because the source search engine is configured to use the word "laptop" as a synonym for "notebook". Hits for both terms were returned in the hit highlighting and extracted by the SWIRL relevancy PostResultProcessor.
Note that the complete content of the SearchProvider's hit highlighting is available for each result in both the body_hit_highlights and title_hit_highlights fields should a use case require it.

Example Search Objects
This query will run the default configuration, which will include 10 results and use of the RelevancyMixer.
{
"query_string": "search engine"
}
As a reminder, this can be run as a GET using the q= parameter:
http://localhost:8000/swirl/search?q=search+engine
Some NOT query examples:
{
"query_string": "search engine -SEO"
}
{
"query_string": "generative ai NOT chatgpt"
}
SWIRL may rewrite these queries depending on the SearchProvider query_mappings. See Search Syntax for more information.
To turn on date sort:
{
"query_string": "search engine",
"sort": "date"
}
To request results be ordered by the date sort mixer, instead of relevancy ranking:
{
"query_string": "search engine",
"sort": "date",
"result_mixer": "DateMixer"
}
Here is the first example with spellcheck turned on:
{
"query_string": "search engine",
"pre_query_processors": "SpellcheckQueryProcessor"
}
The SpellcheckQueryProcessor runs prior to federation. The spell-corrected query is then sent to each SearchProvider. Spellcheck is not recommended for use with the Google PSEs (since they will handle it) and is shown here only as an example.
Note that searches which specify properties like "sort", "result_mixer" or "pre_query_processors" must be POSTed to the Search API.
Here's the starting example, modified to request 20 results from source providers 1 and 3 only, with round robin mixer instead of default relevancy, and a retention setting of 1:
{
"query_string": "search engine",
"results_requested": 20,
"searchprovider_list": [ 1, 3 ],
"result_mixer": "RoundRobinMixer",
"retention": 1
}
The retention setting will cause the search to be deleted after 1 hour, assuming the Search Expiration Service is running.
Here are examples that will work if the Funding Dataset is installed:
electric vehicle company:tesla
social media company:facebook
company:slack